路由管理是RocketMQ的核心功能之一,涵盖了订阅管理,连接管理,负载均衡等一系列功能,代码分布在NameServer、Broker、Producer和Consumer等各组件实现中。RocketMQ有一个特色功能:支持灵活的集群工作方式。Broker、Producer和Consumer都能够在运行时动态扩容或缩容,这都要依赖于强大的路由管理模块。
Producer如何投递消息
我们查看投递代码的入口(DefaultMQProducer或者其事务子类TransactionMQProducer),我们以sendMessageInTransaction发送事务型消息为例,可以看到最终调用了DefaultMQProducerImpl类的sendDefaultImpl方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
private SendResult sendDefaultImpl(
Message msg,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final long timeout
) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
//...省略代码...
//先从本地存储的路由信息表获取topic的路由信息
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic());
//...省略代码...
String lastBrokerName = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName();
//获取具体的路由信息
MessageQueue mqSelected = this.selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName);
//...省略代码...
//
sendResult = this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout - costTime);
//...省略代码...
}
//获取本地路由表
private TopicPublishInfo tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(final String topic) {
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
if (null == topicPublishInfo || !topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
//若当前topic的本地路由表信息不存在,则构建对象,标识当前topic存在路由信息
this.topicPublishInfoTable.putIfAbsent(topic, new TopicPublishInfo());
//从NameServer中远程获取相关信息,并做本地路由表维护
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic);
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
}
if (topicPublishInfo.isHaveTopicRouterInfo() || topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
return topicPublishInfo;
} else {
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, true, this.defaultMQProducer);
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
return topicPublishInfo;
}
}
由于对路由表的管理比较复杂,所以后面单独讲解,我们此处只需要知道其对topicPublishInfoTable等路由信息进行了维护更新。我们接着看selectOneMessageQueue,通过tryToFindTopicPublishInfo获取到当前topic的路由的发布信息对象TopicPublishInfo后,其最终会调用到TopicPublishInfo#selectOneMessageQueue:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class TopicPublishInfo {
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue() {
int index = this.sendWhichQueue.getAndIncrement();
int pos = Math.abs(index) % this.messageQueueList.size();
if (pos < 0)
pos = 0;
return this.messageQueueList.get(pos);
}
}
可以看出,最终返回的MessageQueue对象即为具体的路由信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class MessageQueue implements Comparable<MessageQueue>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6191200464116433425L;
private String topic;
private String brokerName;
private int queueId;
}
最后通过MessageQueue中的信息获取brokerAddr后,最终调用MQClientAPIImpl#sendMessage将消息发送出去。
顺序性投递
发送端有序
因为RocketMQ支持生产者在投放消息的时候自定义投放策略,我们实现一个MessageQueueSelector接口,使用Hash取模法(如ID%队列数量)来保证同一个业务(比如订单)在同一个队列中就行了。
存在问题:当Broker有变动的时候,可能会照成短暂的部分数据的无序性。
消费端有序
RockerMQ的MessageListener回调函数提供了两种消费模式,有序消费模式MessageListenerOrderly和并发消费模式MessageListenerConcurrently。
实际上,每一个消费者的的消费端都是采用线程池实现多线程消费的模式,即消费端是多线程消费。虽然MessageListenerOrderly被称为有序消费模式,但是仍然是使用的线程池去消费消息。
MessageListenerConcurrently是拉取到新消息之后就提交到线程池去消费,而MessageListenerOrderly则是通过加分布式锁和本地锁保证同时只有一条线程去消费一个队列上的数据。
顺序性消费一个很大的弊端是使用了很多锁,而且当前者消费失败后,会阻塞后续的消费。
NameServer
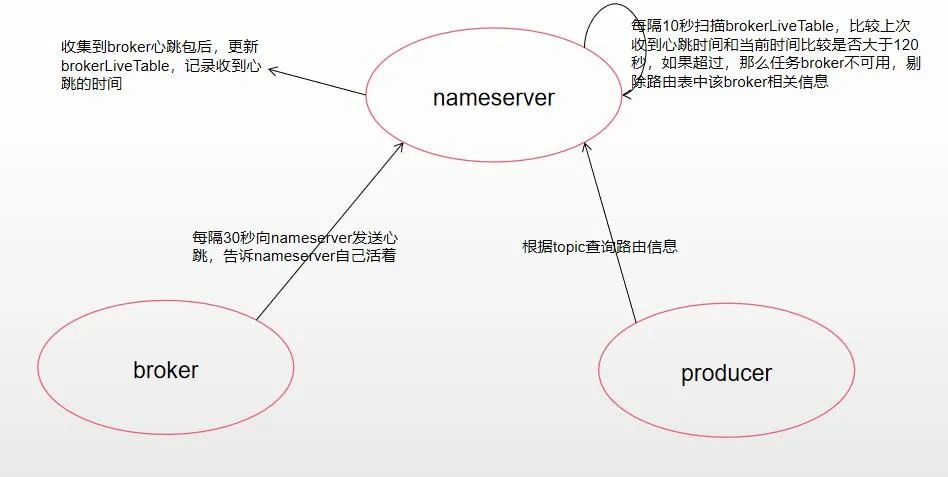 路由发现不是实时的,路由变化后,NameServer不主动推给客户端,等待producer定期拉取最新路由信息。当路由发生变化时通过在消息发送端的容错机制来保证消息发送的高可用。
路由发现不是实时的,路由变化后,NameServer不主动推给客户端,等待producer定期拉取最新路由信息。当路由发生变化时通过在消息发送端的容错机制来保证消息发送的高可用。
多个NameServer服务器之间不进行通信,这样路由信息发生变化时,各个NameServer服务器之间数据可能不是完全相同的,也是通过发送端的容错机制保证消息发送的高可用。
NameServer每隔10s扫描BrokerLiveTable,连续120s没收到心跳包,则移除该Broker并关闭socket连接,broker正常下线也会触发路由剔除;